| |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
Background |
| |
|
| |
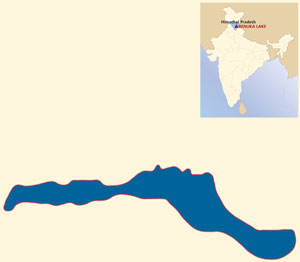
Renuka Wetland is one of the most attractive natural wetlands of Himachal. The wetland is situated at an altitude of 660 meters at a distance of about 37 kms. from Nahan in district Sirmaur. From a distance, the lake looks like a woman sleeping on her side. The lake is home to at least 443 species of fauna and has a circumference of 3,200 meters, with depth varying from 1m to 13m. The Ministry of Environment and Forests Government of India has recognized it as National Wetland in November 2005. The State Government has also declared an area comprising 402 ha. in and around of this wetland as Wild Life Sanctuary.
Delhi government and Himachal government signed an agreement in 1994, regarding the proposal for construction of Renuka dam project. Certain objections were raised by Renuka Bandh Jan Sangharsh Samiti, formed by the residents, regarding the destruction of ecology and biodiversity due to construction of the dam. The Delhi Jal Board released Rs.300 crore to the Himachal Government for purchase of land for construction in 2008. Payment of Eco-System Services (PES) will be used for conservation of the natural resources in catchment areas. 10% will be taken as PES, and spent on sustaining the livelihood of people living in catchment areas, so that the source of water is not disturbed.
The Renuka wetland is dying due to siltation, pollution and growth of weeds. The total area covered by water has reduced by over 25 per cent in 2006. Silt from eroded soil that ran into the lake from surrounding hills and the rapid growth of weeds shrank the lake by almost a quarter. Rapid urbanization and development activities around the Renuka Lake have put tremendous pressure on it. In a study conducted by the Geology Department, Punjab University, it was found that the lake is gradually shrinking and silting is increasing at a rate of 3.3 mm annually.
In 2004, a network of check dams and other civil works was built to check soil erosion. Retaining walls to prevent silt from entering the waters are also built. In 2006, an action plan, of Rs.18 crores, was prepared by State Council for Science, Technology and Environment, Shimla (SCTE) to save the lake from siltation, pollution and growth of weeds. Under the plan, the council proposed to undertake more mechanical and vegetative measures in the catchment to slow down its ageing process.
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
| Links |
Down to earth
Waterbullying to sink 20 villages
Research paper:
Geochemistry of Renuka Lake and wetland sediments, Lesser Himalaya (India):
Implications for source-area weathering, provenance
Environmental Geology, Issue Volume 54, Number 1 / March, 2008
Read more...
Information Sheet on Ramsar Wetlands (RIS)
Bibliography:
Renuka wetland: a newfound abode for migratory birds in Himachal pradesh, Mohan, L. Sharma, R. M. Tak, P. C. , 2005, VOL 131; NUMB 2, pages 163-169.
Book:
Fauna of Renuka Wetland (Himachal Pradesh); 2000; The Director, Zoological Survey of India (ed); 187 p.
|
|
| |
| PEOPLE |
| |
Government:
State Council for Science, Technology & Environment (H.P)
HP B-34 SDA Complex Kasumpti
Shimla-171009 HP India
Phone: 91-177-2622489, 2622490
Tele Fax: 91-177-2620998
Researchers:
Brijraj K. Das and Parkash Kaur
Centre of Advanced Study in Geology,
Panjab University,
Chandigarh, 160014, India
Birgit Gaye
Institute of Biogeochemistry and Marine Chemistry,
University of Hamburg,
Bundesstrasse 55, 20146
Hamburg, Germany
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|